Allowances is a term that helps employees to manage expenses like travelling, cost of living, housing and more. An employee must have come across with words like Dearness Allowance, House Rent Allowance, Conveyance Allowance, Leave Travel Allowance in their salary slips. Having a comprehensive understanding of each allowance will eventually help employees plan their finances better and make the most of their earnings.
The blog will discuss allowance meaning, its types, tax implications, and its significance in salary structures, especially with reference to terms like dearness allowance for central govt employees, travel allowance, and leave travel allowance.
What is an Allowance?
An allowance is a fixed amount of money given by the company to an employee to meet their specific expenses or compensate for certain conditions of employment. Allowance is often added to the basic salary and is typically structured to align with the employee’s role, duties, or living conditions.
Allowances in Salary Structure
Allowances involved in a salary structure form an important part of an employee’s total compensation. Allowance is given to cater to specific needs like housing, transport, or cost of living adjustments like the dearness allowance. The inclusion of allowances helps employers attract and retain talent while optimising the tax benefits for both parties.
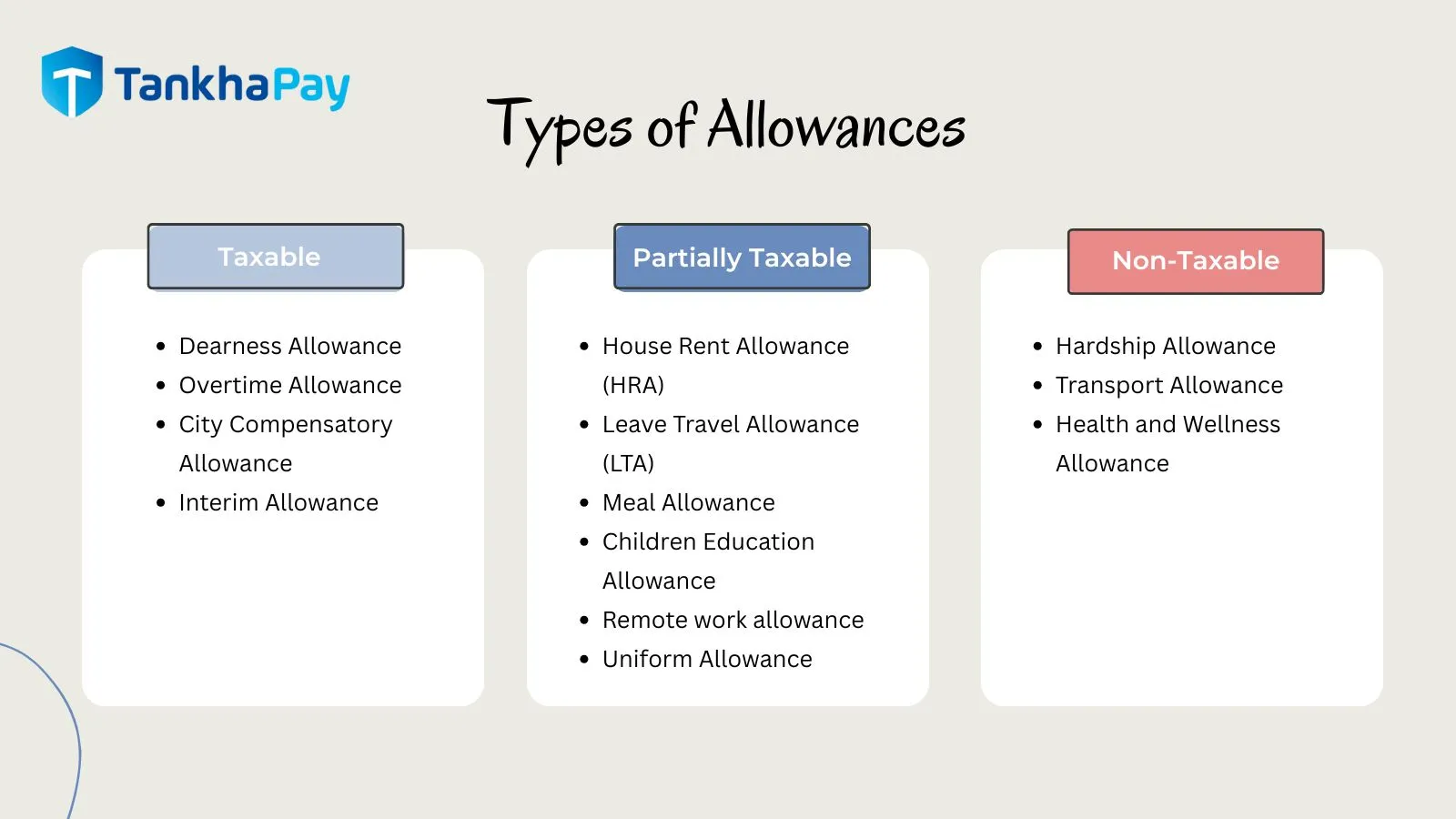
Types of Allowances in Payroll
The payroll system in India comprises various allowances, including:
- Dearness Allowance (DA)
- Conveyance Allowance
- Special Allowance
- Sumptuary Allowance
- Overtime Allowance
- City Compensatory Allowance
- Interim Allowance
- House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Hardship Allowance
- Transport Allowance (TPT Allowance)
- Uniform Allowance
- Children Education Allowance
- Health and Wellness Allowance
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- Meal Allowance
- Remote work allowance
- Children Education Allowance
Taxation of Allowances in India
Taxable Allowance
These are allowances that are fully taxable under the Income Tax Act. Examples include:
- Dearness Allowance is fully taxable if it is not part of retirement benefits. It is a cost of living adjustment paid mainly to government employees and some private sector staff to offset inflation.
- Overtime Allowance is paid for extra hours of work beyond the regular working schedule, overtime allowance is fully taxable as it is considered additional compensation.
- City Compensatory Allowance is provided to employees working in metropolitan or Tier-1 cities to compensate for the higher cost of living. Despite its purpose, CCA is entirely taxable.
- Interim Allowance is a temporary allowance given in anticipation of a revised pay structure.
Partially Taxable Allowance
These allowances are partially exempt from tax, subject to certain conditions:
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): HRA is provided to employees living in rented accommodation. The amount varies depending on the city of residence—higher for metro cities due to higher living costs.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Covers expenses incurred during domestic travel for holidays (leave travel allowance exemption rules apply). The leave travel allowance exemption can be claimed under specific conditions and usually requires actual travel proofs and documentation.
- Meal Allowance: A meal allowance is provided to employees to cover food expenses during work hours or while on official duty. In some cases, this may be offered via food coupons or digital cards. Tax exemption may apply up to a limit if structured properly.
- Children Education Allowance: A small but significant allowance for educational expenses. It is exempt up to a certain limit (currently ₹100 per month per child for up to two children) and is particularly beneficial in easing educational expenses for families with children going to school.
- Remote work allowance: This allowance is relatively a newer form of allowance given to cover expenses such as internet bills, electricity, and office supplies while working remotely.
- Uniform Allowance: This is paid to employees who are required to wear uniforms while performing their job duties. This allowance is exempt from tax to the extent it is actually spent on purchasing and maintaining the uniform.
Non-Taxable Allowance
Some allowances are fully exempt from income tax, such as:
- Hardship Allowance: Hardship Allowance is provided to employees working in challenging, remote, or hazardous conditions such as extreme climates, high-risk zones, or isolated areas. It compensates for physical or psychological strain caused by the work environment.
- Transport Allowance (TPT Allowance): Provided for daily commuting costs, with Transport Allowance Tax Exemption under specific limits. While similar to Conveyance Allowance, this allowance is often structured separately.
- Health and Wellness Allowance: Health and Wellness Allowance is offered to promote employee well-being by offering expenses for gym memberships, fitness classes, or a routine health check-ups. Some companies extend this to mental health support and therapy sessions.
Difference between Allowance and Salary
While the salary is a fixed, regular payment, allowances are supplementary amounts meant to cover specific expenses or needs. Salary is generally taxable in full, whereas allowances may enjoy tax exemptions.
| Salary | Allowance |
|---|---|
| A fixed, regular amount made by an employer to an employee for work performed. | An additional amount paid to cover specific expenses such as housing, travel, or cost of living. |
| Compensation for work done. | Support for specific personal or work-related expenses. |
| Generally fully taxable as per income tax laws. | May be fully taxable, partially taxable, or fully exempt, depending on the type. |
| Basic Pay, Gross Salary | Dearness Allowance, House Rent Allowance, Conveyance Allowance, Leave Travel Allowance |
| Major component of CTC (Cost to Company). | Added to CTC to provide extra financial benefits. |
Importance of Allowances in Employee Compensation
Allowances contribute to the total cost to company (CTC) and affect the net income of employees. They usually include
- Providing financial support for specific needs.
- Boosting employee satisfaction.
- Offering tax-saving opportunities.
- Increasing transparency in pay structure.
For example, the central government dearness allowance is a major part of government employees’ income and is regularly revised based on inflation.
How can employers structure allowances effectively?
Structuring allowances effectively for employees will ultimately benefit are both; employee and employer with meaningful advantages and cost effective. For employers, the goal is to balance employee satisfaction with financial and legal efficiency. By providing dearness allowance, house rent allowance, conveyance allowance, and special allowance strategically, organisations attract and retain skilled talent and also offer tax-optimised salary structures. Structured allowances results in:
- Attracting and retaining talent.
- Ensuring compliance with tax laws.
- Minimising payroll costs via tax-efficient components.
- Aligning benefits with employee needs (e.g., travel allowance for field staff).
How to Calculate Allowances in Salary?
Calculating allowances in a salary involves identifying the applicable types of allowances, determining their values, and assessing their tax implications. The process may vary based on the nature of the allowance and the employer’s compensation structure.
- Identify Allowances Applicable to the Role- Begin with listing out all allowances relevant to the employee’s position. This may include Dearness Allowance, House Rent Allowance, Conveyance Allowance, Leave Travel Allowance, and more. For instance, a field executive may be eligible for a travel allowance, while an urban office-based employee might receive a higher transport allowance.
- Determine the Calculation Basis- Allowances are often calculated as a percentage of the basic salary or a fixed amount.
- Apply Exemption Limits (if any)- Certain allowances have prescribed exemption limits under the Income Tax Act.
- Include Fully Taxable Allowances- Any allowance that does not qualify for exemption—like AD Allowance, overtime pay, or meal allowances—must be added to the taxable portion of the salary.
- Finalise the Gross and Net Salary-
- Gross Salary = Basic Salary + All Allowances
- Taxable Salary = Gross Salary – Exempted Allowance Components
- Net Salary = Taxable Salary – Deductions (like Provident Fund, TDS, etc.)
This calculation ensures transperancy in structuring payroll, aligns with statutory norms, and provides transparency for both employees and tax authorities.
Common Misconceptions about Allowances
Despite being a standard component of most salary structures, allowances are often misunderstood by employees and even employers. Let’s take a look at some of the common misconceptions about allowances:
- All allowances are tax-free- One of the most common myths is that all allowances are exempt from tax. But in reality, many allowances, such as dearness allowance, ad allowance, and special allowance are fully taxable. Some of the specific allowances like house rent allowance and leave travel allowance are qualified for partial exemption under particular conditions.
- Allowances are the same as reimbursements- While allowances are fixed, periodic payments given irrespective of actual expenses incurred, reimbursements require submission of bills or proof of spending.
- Higher allowances always mean higher take-home pay. Since several allowances are taxable, increasing them may also increase taxable income, thereby reducing net take-home pay. That is why structuring allowances is very important.
- Allowances are uniform across all companies- No, allowances are not same across all companies. Allowances are different based on companies, sectors, and designations (job role).
- Allowances don’t affect retirement benefits- Some allowances like dearness allowance are included when calculating pension or provident fund contributions, while others like house rent allowance or lta allowance are excluded.
- Allowances can be randomly added or removed- Allowances should be structured as per company policy and compliance requirements.
- All employees are entitled to the same set of allowances- Allowance eligibility is usually based on factors like employees designation, grade pay, location, and roles and responsibilty. Field staff may receive a travel allowance, while office-based employees may be entitled to a TPT allowance (transportation allowance).
- LTA covers all kinds of travel expenses- Leave Travel Allowance only covers travel within India and does not include hotel stays, food, or local transport during the vacation.
- ‘Allowance’ only refers to employee benefits- Allowance is commonly linked with salaries and employee benefits. Yet the term can apply to other contexts too, like Air India baggage allowance refers to luggage limits, not compensation.
Clarifying these myths will be beneficial for both; employers and employees better understand the importance of allowances in salary, compliance, and financial planning. Proper knowledge leads to better utilisation of available benefits and minimises the risk of tax related issues.
Frequently Asked Questions on Allowances
What are allowances in salary?
Allowances are additional financial benefits provided over the basic salary to cover specific expenses or living conditions.
What is a monthly allowance?
It is a fixed monthly payment for certain expenses like transport allowance, dearness allowance, or HRA allowance.
How is the taxable income calculated?
Taxable income is calculated by adding all the income, including taxable allowances like dearness allowance and special allowance, and then subtracting the eligible exemptions and deductions.
What is a position allowance?
A position allowance is a type of special allowance granted to employees based on the level of responsibility or the nature of the role they hold. It is often seen in leadership or high-impact roles and is generally taxable.
What is Dearness Allowance?
Dearness Allowance (DA) is a cost-of-living adjustment allowance paid to employees, particularly those in the public sector, to lessen the pressure of inflation.
What is Conveyance Allowance meaning?
Conveyance Allowance is paid to employees to cover transportation expenses between their home and workplace.
What is LTA Allowance?
LTA Allowance or Leave Travel Allowance is a part of salary provided to employees to cover travel expenses incurred during leaves.
What is sumptuary allowance?
Sumptuary allowance is a type of allowance granted to certain government officials such as judges, high ranking civil servants, and constitutional members, to cover expenses related to official hospitality, representation, and ceremonial duties. It aims to help maintain the decorum and dignity that comes with their position.
What is Special Allowance in salary?
Special Allowance is a residual salary component paid to employees for performance, incentives, or specific roles.
Are allowances part of the CTC (Cost to Company)?
Yes, all types of allowances—Dearness Allowance, LTA, HRA, Conveyance Allowance, and more—are part of the CTC, as they form part of the total compensation offered by the employer.