The salary slip, also known as a payslip, serves as an official document outlining an employee’s earnings and deductions. Each month, employees receive pay slips from their employers, detailing essential information such as the company’s name, the employee’s designation, location, and bank details.
Within the salary slip, there are key components. Earnings, including basic pay, dearness allowance, house rent allowance, medical allowance, and special allowance, are outlined. Additionally, deductions such as professional tax, tax deduction at source, and employee provident fund are also specified. It’s important to note that these details can vary from one company to another.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the significance of the salary slip or pay slip, explaining its importance in the financial context. We’ll also provide insights into how to create a simple salary slip format using Excel, a commonly used tool for such tasks. Furthermore, we’ve curated various salary slip formats in Excel, Word, and PDF for your convenience, ensuring you have a range of options to choose from.
What does Salary Slip mean?
A salary slip can be defined as a document that contains the details of an employee’s salary. These details include the basic pay, bonuses, deductions, etc., that are given to the employee every month by the employer. The employees often get soft copies of the same and sometimes are given hard copies as well.
EXCEL FORMAT OF SIMPLE SALARY SLIP
The structure and contents of a payslip or salary slip may vary based on the company or the location.
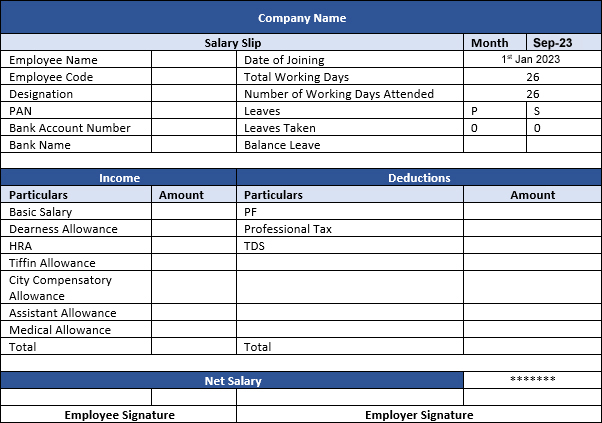
Download Different Simple Salary Slip Formats
| Formats | Files |
|---|---|
Simple Salary Slip Format in Excel |
Download |
Simple Salary Slip Format in Word |
Download |
Simple Salary Slip Format in PDF |
Download |
Components of Salary Slips or Pay Slips Format
Every month, employees receive their salary slips in PDF formats, yet comprehending the intricate details of a salary slip often proves challenging. It’s not just a document for loan applications; it holds substantial importance in various aspects of financial management.
- Informed Job Switching: Understanding your salary slip empowers you to compare job offers effectively. By deciphering the components, you can make informed decisions when switching jobs, ensuring you get the best deal.
- Tax Optimisation: A detailed grasp of your salary slip allows you to optimise your tax liability. By identifying the deductions available, you can strategically plan your finances, minimising your taxable income and maximising your savings.
- Grasping Savings: Within the confusing jargon of a salary slip lie details about your forced savings, such as contributions to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI). Understanding these deductions helps you comprehend your overall financial commitments and savings.
In the salary slip’s income section, essential components include the Basic, constituting 35-50% of the salary. At junior levels, Basic is higher, while as employees progress, other allowances increase. Organisations often maintain a lower Basic to prevent topping up the allowance pay. Basic, 100% taxable, appears first in the earnings section.
A salary slip isn’t just a list of numbers; it’s a blueprint of your financial dealings with your employer. Mastering its format and components is pivotal for making sound financial decisions and ensuring you’re in control of your earnings and investments.
Basic Salary
This core element serves as the bedrock of an employee’s income structure. While it constitutes a significant portion of the salary, its taxable nature necessitates careful financial planning. At entry levels, basic pay tends to be relatively higher, gradually giving way to other allowances as one climbs the organisational ladder.
Dearness Allowance (DA)
Dearness Allowance (DA) is a dynamic component directly influenced by the cost of living adjustments due to inflation. Its variations cater to diverse locations, ensuring fair compensation relative to the local economic conditions. Although taxable, DA attempts to balance the employee’s purchasing power against rising prices.
House Rent Allowance (HRA)
House Rent Allowance (HRA) accommodates employees residing in rented accommodations. Its tax exemptions, calculated based on rent paid, provide financial relief. The exemptions, governed by specific percentages and rent-payment criteria, empower employees to optimise tax savings based on their living arrangements.
- For rented homes: 50% (metros) or 40% (others) of Basic.
- Tax exemption criteria:
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of pay (Basic + DA).
- Actual HRA received.
- 50%/40% of (Basic + DA) based on city.
Conveyance Allowance
Commuting is a daily reality for employees. Conveyance allowance acknowledges these expenses, offering tax exemptions up to a certain limit. For many, it represents an essential financial relief, making the daily journey to work more financially manageable.
Exempt up to ₹ 1600/month or actually received in earnings.
Medical Allowance
Catering to healthcare needs, medical allowance assists employees in covering medical expenses. Tax exemptions, contingent upon the submission of medical bills, encourage employees to maintain their health and well-being. The allowance underscores the employer’s commitment to employee welfare.
Exempt up to ₹ 15,000/year if proof is submitted.
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is a testament to the employer’s acknowledgement of employees’ need for leisure and family time. Offering tax benefits for travel, LTA fosters a healthy work-life balance. Its block-based calculation aligns with employees’ travel aspirations, ensuring periodic opportunities for rejuvenation.
Special Allowance
Special allowances act as powerful motivators, encouraging employees to excel in their roles. While fully taxable, they signify the organisation’s recognition of exceptional performance. These allowances are often tailored to individual job roles, acknowledging and rewarding specific skills and achievements.
Understanding these components sheds light on your salary slip, demystifying the financial intricacies within.
Deductions
- Provident Fund (PF): PF acts as a valuable savings tool for employees, managed under the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. Employees contribute a fixed percentage of their salary, matched by the employer, forming a secure fund managed by the Employees Provident Fund Organization.
- Professional Tax: This state-imposed tax is levied on all citizens earning income, varying in amount across states. It’s a mandatory contribution that individuals make from their earnings, ensuring financial support for state initiatives.
- Tax Deductible at Source (TDS): TDS represents the amount deducted from a salary at the source of payment. The entity making the payment deducts this tax, ensuring compliance with tax regulations. The recipient of the income is accountable for this tax, streamlining the taxation process.
- ESI: Employee State Insurance (ESI) is a social security scheme that safeguards employees during challenging circumstances. ESI deductions are calculated based on the gross salary paid to employees. According to the ESI Act, the employer contributes 3.25% of the wages, while the employee contributes 0.75% of the wages to the contributory fund. This joint contribution creates a financial safety net, ensuring that employees have access to essential benefits and medical care when they need it the most.
Formulas of Salary Slip Format
Below, we have tabulated some of these set Excel formulas of Simple Salary Slip Formats. It will help you to calculate the Gross earnings along with the deductions.
| Particulars | Formula |
|---|---|
| Taxable Income | Gross Salary – Deductions |
| CTC= Total salary package of the employee | Gross Salary + EPF + Gratuity + Others |
| Gross Salary | Basic Salary + HRA + Other Allowances |
| Net Salary | Basic Salary + HRA + Allowances – Income Tax – Employee’s Provident Fund – Professional Tax |
CTC vs. Gross Salary
Here is the fundamental difference between CTC and Gross Salary:
| CTC | Gross Salary |
|---|---|
| CTC stands for Cost to the Company and encompasses the comprehensive expenditure a company incurs while employing an individual. | The gross salary constitutes the total payment made to an employee before tax deductions while also accounting for deductions like the Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI). |
| This includes incorporating direct benefits, indirect perks, and savings contributions in the overall package offered to the employee. | This sum is derived by subtracting elements such as provident fund, ESI, gratuity, and income tax from the Cost to the Company (CTC). |
Why are Salary Slips or Pay Slips Important?
Salary slips can be very crucial in the professional world. They serve as the legal proof of you being a salaried employee. It would be of great help to always keep them safe as you would with other significant documents.
Here are some other reasons:
Proof of Employment
Pay slips bear the weight of credibility in various official contexts. Whether applying for travel visas, university admissions, or undergoing background checks, a salary slip validates an individual’s professional standing. It not only affirms current employment but also delineates the career trajectory, offering a comprehensive snapshot of an individual’s designation within the organisation and their overall employment history.
Strategic Income Tax Planning
Beyond their role in employment validation, salary slips serve a critical purpose in income tax planning. The provision of a detailed breakdown of earnings and deductions, these documents empowers employees to strategise their tax liabilities effectively. From basic salary to allowances and deductions such as Professional Tax, EPF, and TDS, salary slips offer insights that enable individuals to calculate TDS returns accurately. Furthermore, they aid in maximising benefits from tax deductions, rebates, and allowances within the legal boundaries stipulated by the Income Tax Act of 1961. Effectively managed tax planning ensures financial prudence and enables individuals to navigate the complexities of the taxation system with confidence.
Navigating Salary Negotiations and New Employment Opportunities
Salary slips become invaluable assets during salary negotiations and when exploring new employment opportunities. When engaging in negotiations with prospective employers, past salary slips provide a tangible foundation for discussions. They offer a clear historical perspective, enabling employees to advocate for equitable compensation based on their previous earnings. In the realm of new employment, HR personnel often request these documents for verification purposes, ensuring transparency and credibility in the negotiation process.
Facilitating Financial Transactions and Credit Management
Beyond their role in employment and taxation, salary slips are pivotal in facilitating financial transactions and credit management. When individuals apply for loans, credit cards, mortgages, or other forms of borrowing, financial institutions demand concrete evidence of a stable income. Salary slips offer this assurance, showcasing an individual’s ability to meet monthly payment obligations. They not only set credit limits but also serve as a crucial eligibility criterion for various financial products. In essence, salary slips simplify personal finance management, enabling seamless financial transactions and fostering responsible credit practices.
In Conclusion
Salary slips are crucial documents for all employees to have. But, 93% of Indian employees are unorganised and hence do not get salary slips. They thus cannot avail of loans as they need proof of employment. With the TankhaPay app, employers can not just provide PF & ESI to their workers but also salary slips, which are available to download on the app. So, what are you waiting for, download the TankhaPay app today or visit www.tankhapay.com for more information.
FAQs on Salary Slip
What is the salary slip rate?
The salary slip rate refers to the frequency at which you receive your salary slip. Typically, it aligns with your salary payment cycle, whether monthly, bi-weekly, or otherwise. Confirm this with your HR department for accurate information.
How do I get a salary certificate?
Proof of salary is exactly what it sounds like, proof of the amount you get paid for your job. It is usually validated through your salary slip, bank statements reflecting salary credits, or a salary certificate issued by your employer. Banks, landlords, or any institution requiring this proof will generally accept one of these documents.
How do I verify my salary?
To verify your salary, you can provide your salary slip, bank statements showing salary credits, or request a salary certificate from your HR department.
How can I download my salary slip?
Check if your company provides an employee portal or HR software. If so, log in to your account, navigate to the payroll or salary section, and you should find an option to download your salary slip. If not, a quick request to HR should get you the digital copy you need.
Are Salary Slips Confidential?
Yes, salary slips are confidential documents. Employers are bound to protect their employees' financial information, ensuring it's accessible only to authorised personnel and the respective employees.
What Role Does a Salary Slip Play in Taxation?
Salary slips play a vital role in taxation, serving as proof of income. They aid in calculating taxable income, allowing individuals to file accurate income tax returns and claim deductions as applicable.
How Does Overtime Reflect on a Salary Slip?
Overtime earnings are typically detailed separately on a salary slip, showcasing the extra hours worked and the additional pay received, ensuring transparency in the payment structure.
What Should I Do if There’s an Error on My Salary Slip?
If you notice any discrepancies or errors on your salary slip, it's essential to immediately bring them to the attention of your HR or payroll department for rectification to avoid future complications.
How Long Should I Keep My Salary Slips?
It's advisable to retain your salary slips for at least a few years. They can serve as valuable references during tax audits, loan applications, or for any financial inquiries that may arise in the future.
Also Read
- Payroll Process – Basics, Requirements, Compliances
- HR Policies – A Roadmap for Organisational Success
- What is Payroll Management System? – Definition and Importance






















Dear tankhapay.com admin, Your posts are always well-received by the community.
Excellent article! Will check out more about tankhapay.